Looking for reactive dye definition? You are on the right track! This article is all about reactive dye definition along with its components, influencing factors and most importantly dye hydrolysis.
Stay tunned….
Reactive dye consists of reactive group that makes covalent bonds with the fiber structure. Thus it becomes a distinct part of the fiber. They are highly used for their varying shade range, fastness, brilliancy.
But 50% of reactive dyeing cost is attributed from washing off stages to remove hydrolysed dyes and the treatment for resulting effluent.
Reactive Dye Definition
Reactive dye consists of chromophore and reactive group along with solubilizing and bridging group. This is the only dye class that have reactive group in their structure and forms covalent bond with polymeric system of fiber.
Reactive dye + fiber = Reactive dye-fiber (by covalent bond)
Components of Reactive dye
The different structural components of a reactive dye are:
- A chromogen which is responsible for the color
- Solubilising group that is responsible for the solubility of the dye
- Reactive group that forms covalent bond with fiber polymer
- Bridging group between the reactive group and the chromophoric system
- A leaving group
Let’s think about the general structure of reactive dye-
D-S-R-B-X
Where, D = Dye chromophore (Azo, Anthaquinone, Metal complex, Phthalocyanine group)
S = Solubilising group (-SO3Na)
R = Reactive group (-Cl, -Br, -SH, -OCH)
B = Bridging group (Amino, Oxide, Sulphur, Ethyl, Methyl group)
X= Leaving group
Significance of Chromophore
The variation in chromophore, is quite important factor in case of reactive dye. Here’s the reasons:
- Chromophore is the reason of giving various shade range
- It helps to cover maximum color gamut
- Chromophore affects the reactivity of dye
- It also has impact on substantivity and diffusion co-efficient.
- Thus chromophore helps to determine fixation efficiency and washing- off properties of reactive dye.
Significance of Bridging Group
For chemical synthesis purpose, bridging group is mostly required. It influences some properties of reactive dye. Here’s the factors:
It affects the reactivity of the system. The dissociation of bridge (-NH- -N-) reduces the reactivity of reactive dye. Substantivity can also be reduced.
- The degree of fixation is affected by the length and flexibility of the bridging group.
- Dye-fiber bond stability as well as link between chromogen and reactive group may brake under adverse condition.
Influencing factors in case of Reactive dye
- pH – In case of reactive dye pH is an important factor as dyeing is carried in alkaline pH. pH is maintained at 11-11.5 . In case of reactive dye, fixation is also occurred at alkaline pH.
Chemically cellulose behaves as a polyhydric alcohol and commercial reactive dyes react with it only under alkaline condition. The adsorption of sodium hydroxide by cellulose follows an ionic mechanism that results the cellulose behaving as weak acid that dissociates sodium cellusate.
Reactive dye is absorbed and diffused inside the fiber under neutral condition but do not react with polymeric system of the fiber as the concentration of cellusate ion is extremely low. So, addition of alkali increases the ionic concentration of cellusate ion and promotes the dye-fiber reaction.
As a result, alkaline pH should be maintained for dyeing and fixation purpose.
- Temperature – Temperature is maintained depending on which dye brand we use. For hot brand reactive dye high temperature is required ( 71-93℃ ) whereas for cold brand dyes low temperature is required ( 33-60℃ ) as they are highly reactive.
For fixation purpose, Alkali controllable dyes need temperature between 40 to 60℃ whereas Salt controllable dyes require temperature above 80℃.
- Concentration of electrolyte – Concentration of electrolyte depends on the shade we want. For light shade less electrolyte is required whereas for dark shade huge amount of electrolyte is required.
For example, Practically in industry For light pink shade ( 0.4% ) 5 g\L industrial salt is used whereas for black shade ( 6% ) 20 g\L industrial salt is used. - Time – 60 to 90 min is required for dyeing.
- Liquor ratio– Huge amount of liquor is used for dyeing purpose. The higher the liquor ratio the better the dyeing efficiency achieved.
Hydrolysis of Reactive Dye
When alkaline condition is provided with reactive dye, they easily reacts with the hydroxyl group of cellulose. But if this situation is carried out for too long period, the dye molecules react with the hydroxyl group of water.
This results in concentration drop. Hydrolysis is the reaction that occurs between the dye particle and the hydroxyl group of water. 20-40% dye hydrolysis takes place in case of reactive dye.
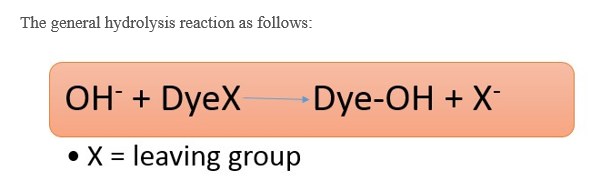
- In case of Triazine dyes


- In case of Vinyl Sulphone dyes

Dye hydrolysis increases with the increasing following parameters:
- pH
- Dyeing temperature
- Time
- Amount of electrolyte
- No of reactive group present in the dye structure
- Reactivity of the dyes
- M:L ratio
How to reduce the dye hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis depends upon the reactivity of reactive groups as well as the no of reactive groups present in the dye structure. For each class of reactive dyes, different application procedure is recommended.
As different class of dyes require different temperature for dyeing. The amount of alkali, temperature during dyeing, pH as well as dyeing time should be kept minimum or low as much as possible.
This can help in reducing dye hydrolysis. The contact time between dye and alkali is necessary for activation in case of reactive dye.
But this contact time should be kept as minimum as possible if you really want to reduce the hydrolysis of reactive dye.
To Wrap Up!
Reactive dyes are not fast to chlorine bleach unlike Vat dyes. Reactive dyed treads can’t be post bleached. Again the cost for washing off process and the effluent treatment process is high for reactive dye.
Although reactive dyes have such limitations, they are considered best for cellulose dyeing. You may also check: Know the trade names of reactive dye in brief!
Salma Hasin the author of this site completed her BSc. in Textile Engineering (Wet Processing Engineering). She wants to share her knowledge to help students in their studies and businessman & entrepreneurs in their businesses in making wise decisions fast.

